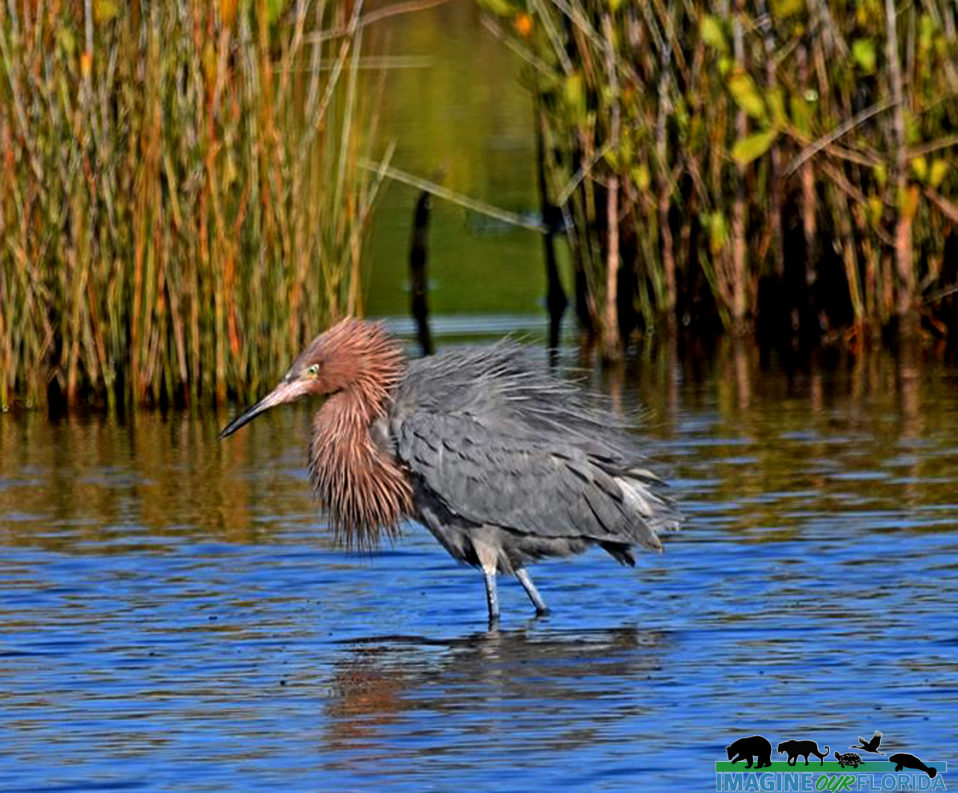
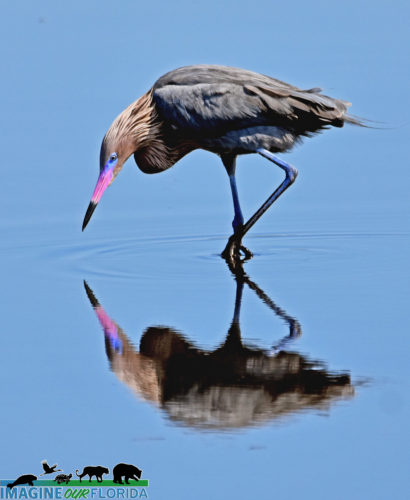
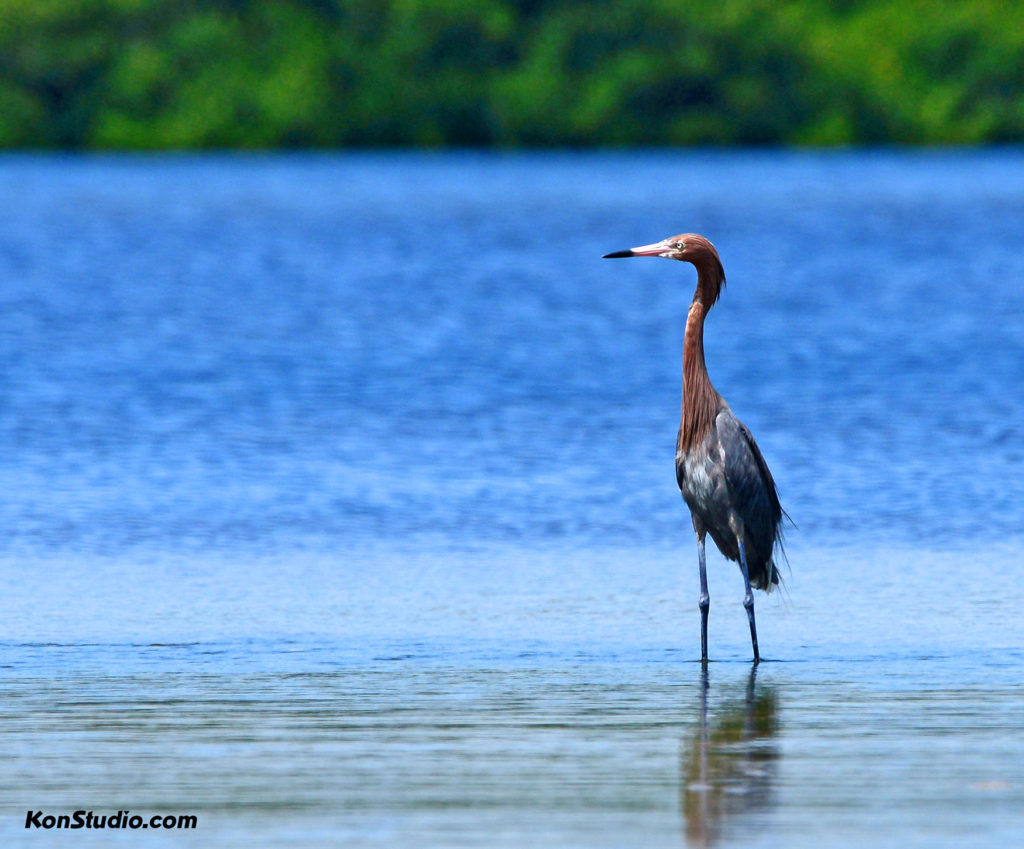
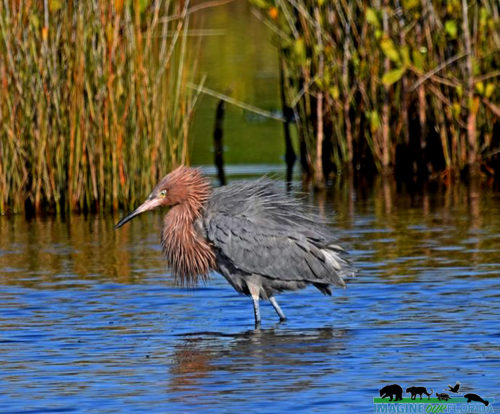
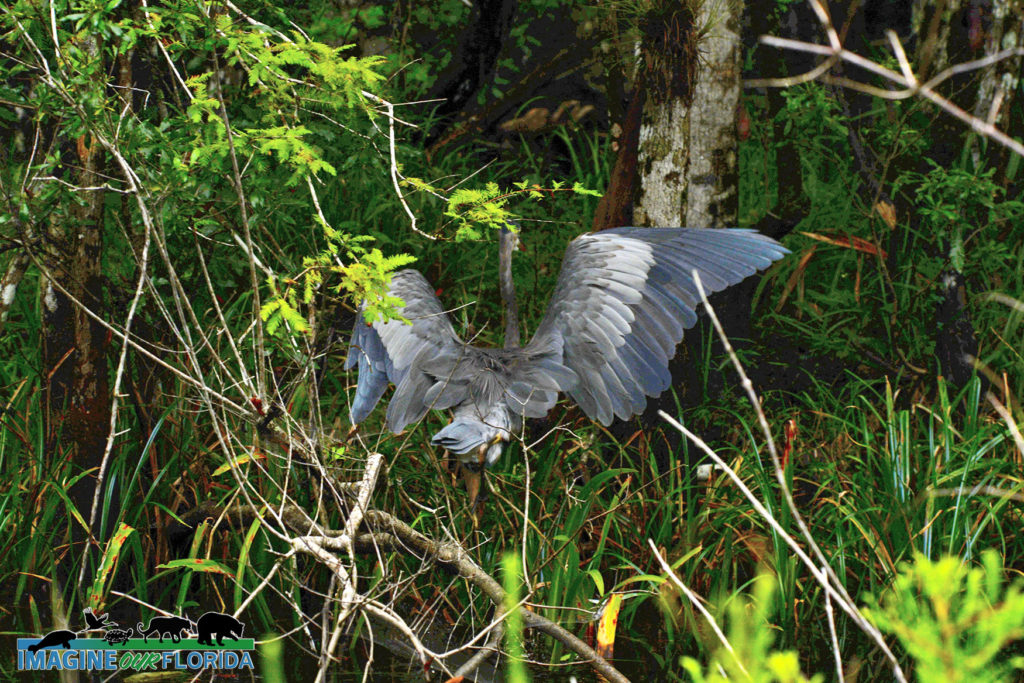
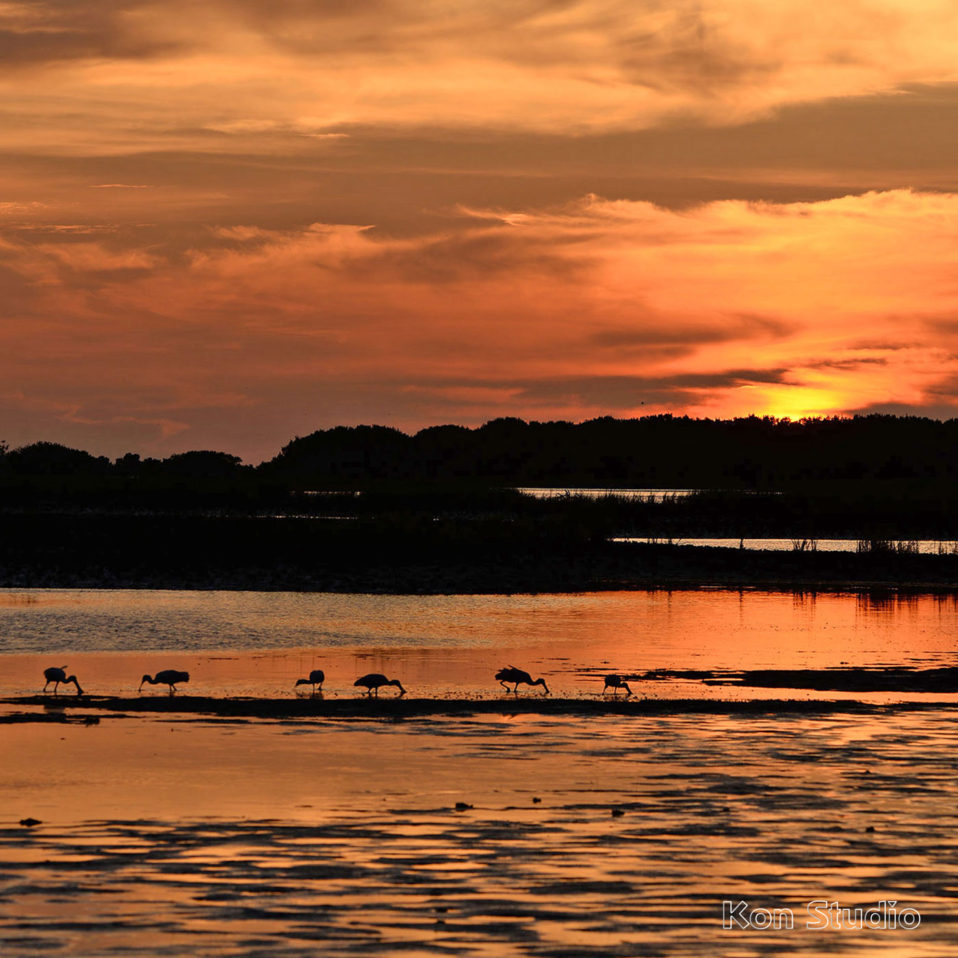
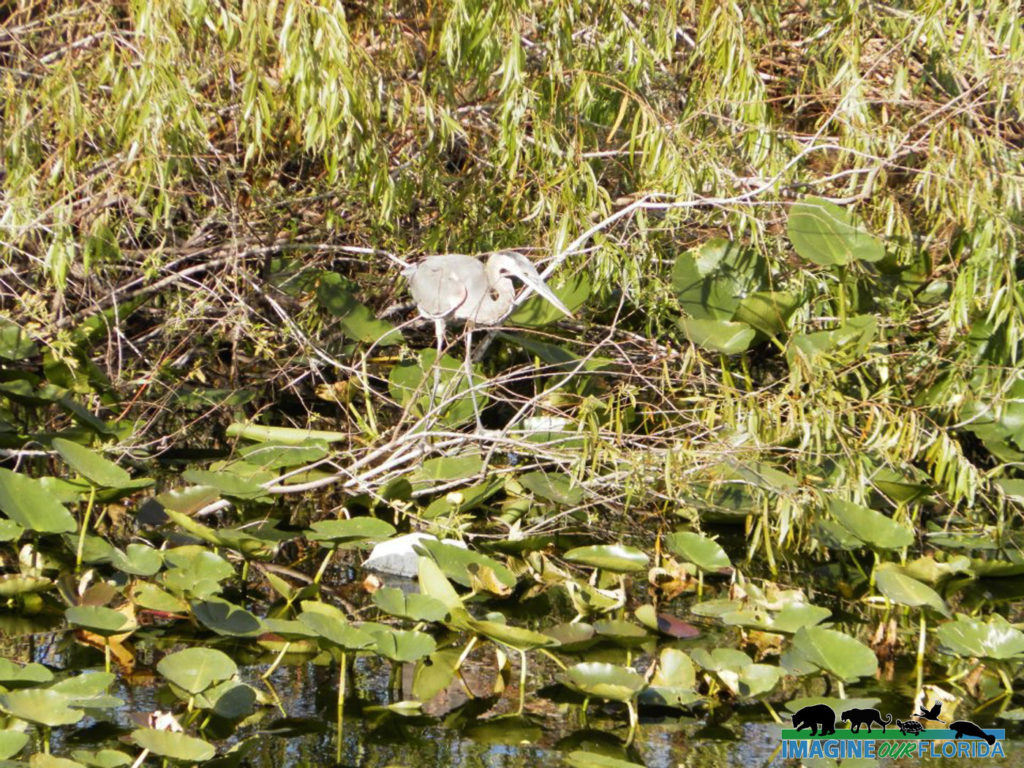
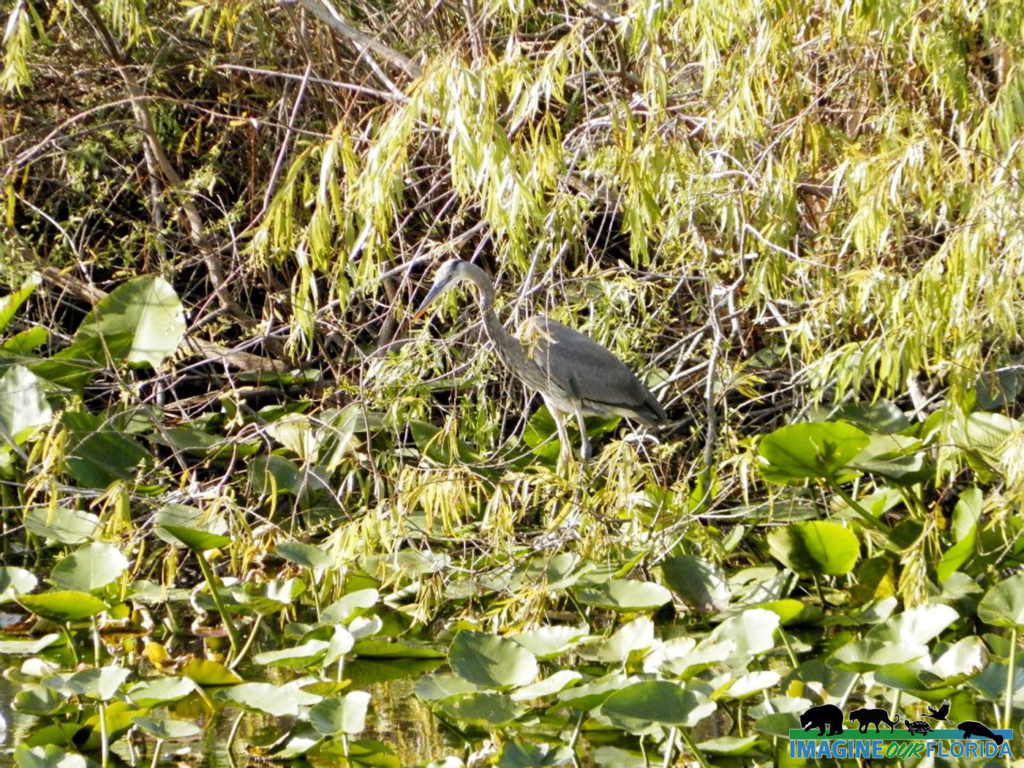
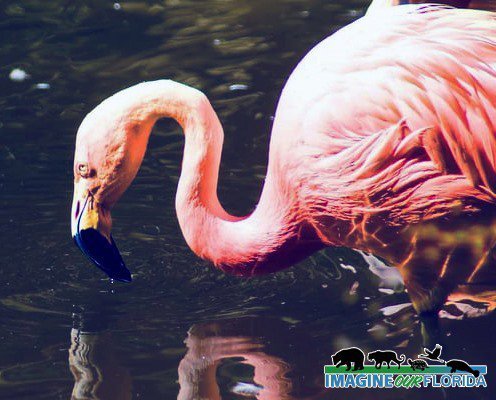
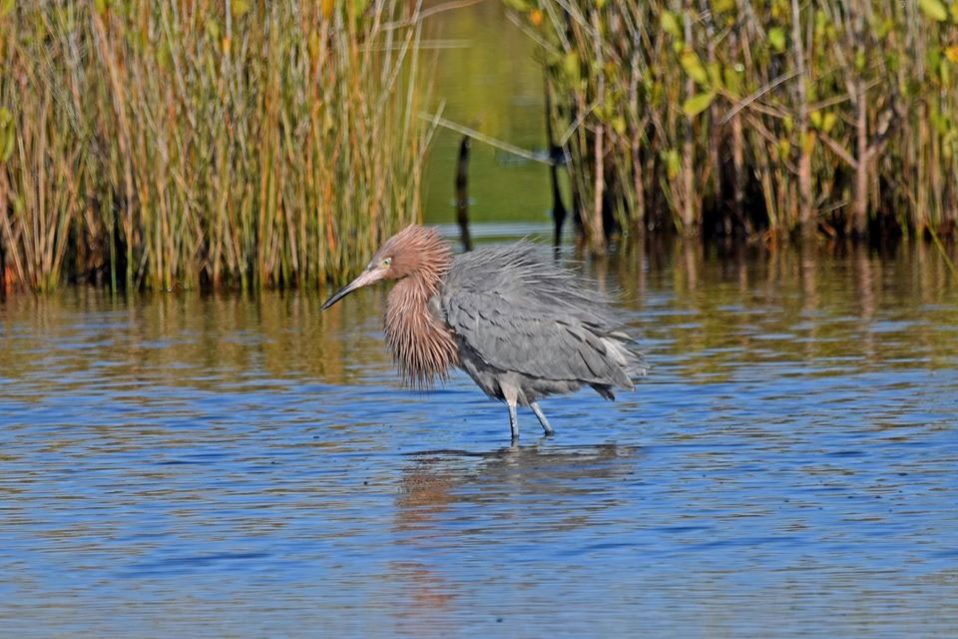
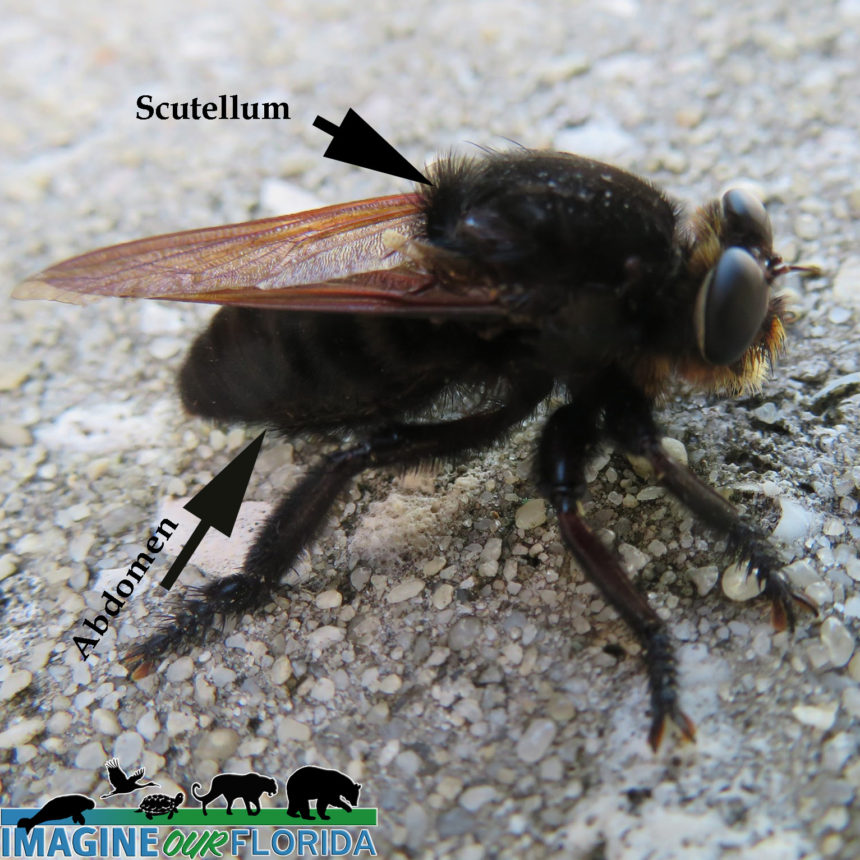
Reddish Egrets, (Egretta rufescens), can be found running and jumping in the shallow saltwater of Florida coasts. Estuaries, lagoons, and waters near mangroves provide a variety of small fish that are brought to the surface by the egret’s intricate dance of jumps, spins, and footwork with wings of 46-48 inches spread open.
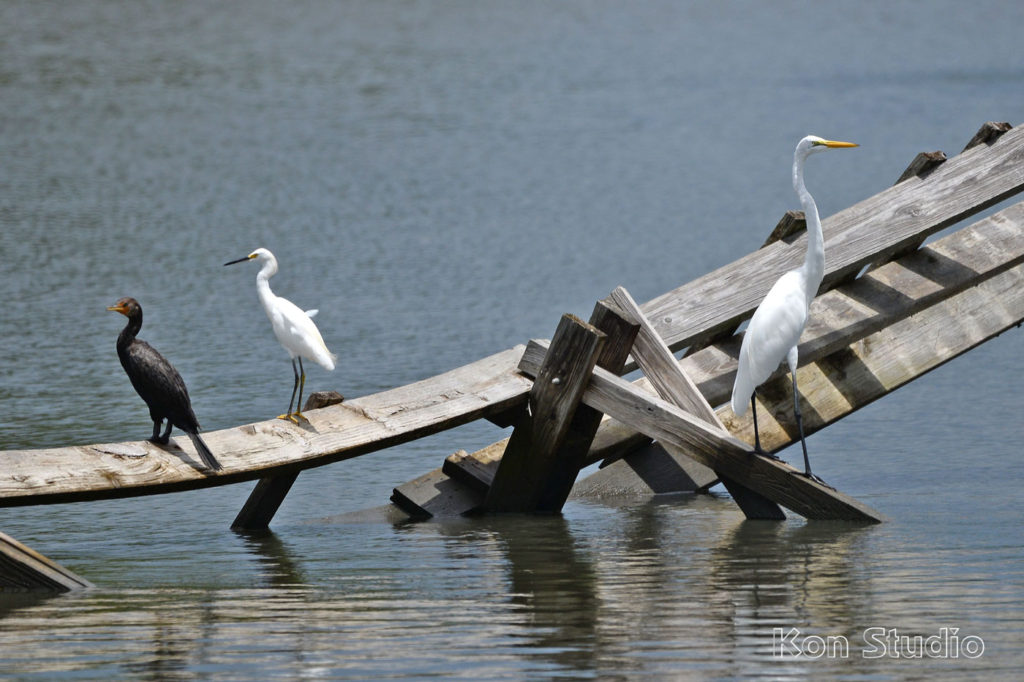
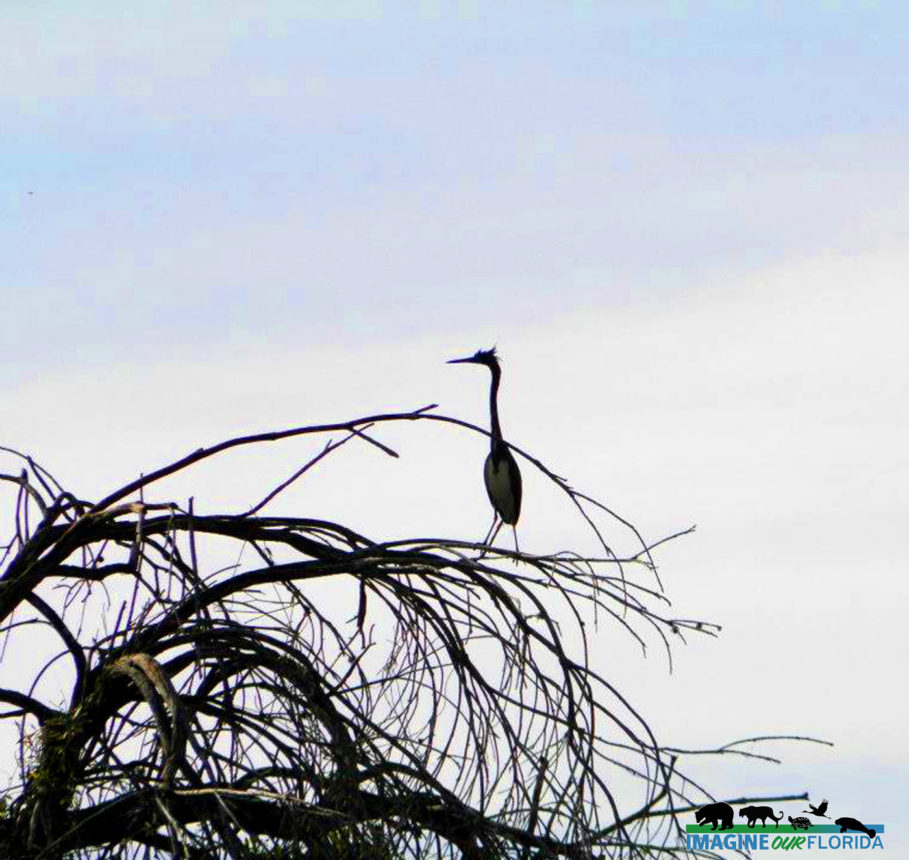
A dark Reddish Egret is pictured here. You may also discover a white morph that has a mostly white body. They both have a black-tipped pink bill and blue feet and legs.
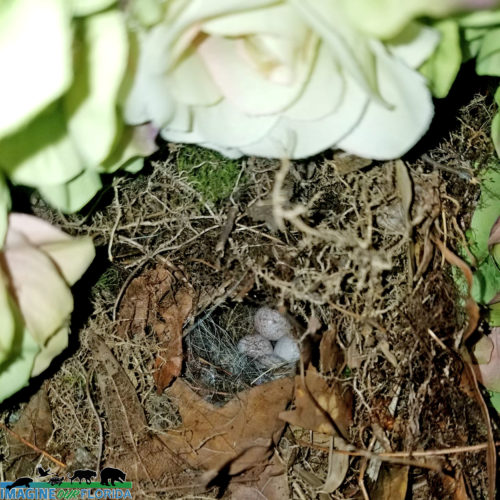
Reddish Egrets breed in mainland Florida between February and June. Breeding in the Keys and Florida Bay occurs from November to May. Both the male and female incubate three to four eggs for 26 days. The young leave the nest within 45-49 days after hatching.
Plume trading nearly wiped out the Reddish Egrets. The Reddish Egret is currently State designated as Threatened and is protected by the U.S. Migratory
Bird Treaty Act.
Today, the Reddish Egret population may be in decline once again. Development, degradation of habitat, loss of genetic diversity, human disturbance, and predators are cause for concern.
You can be their voice. Advocate for clean water and the protection of land where Reddish Egrets call home. Respect their right to share our state with us. Give them space, observe from afar, and be mindful of where you hike, boat, and play.



































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Recent Comments