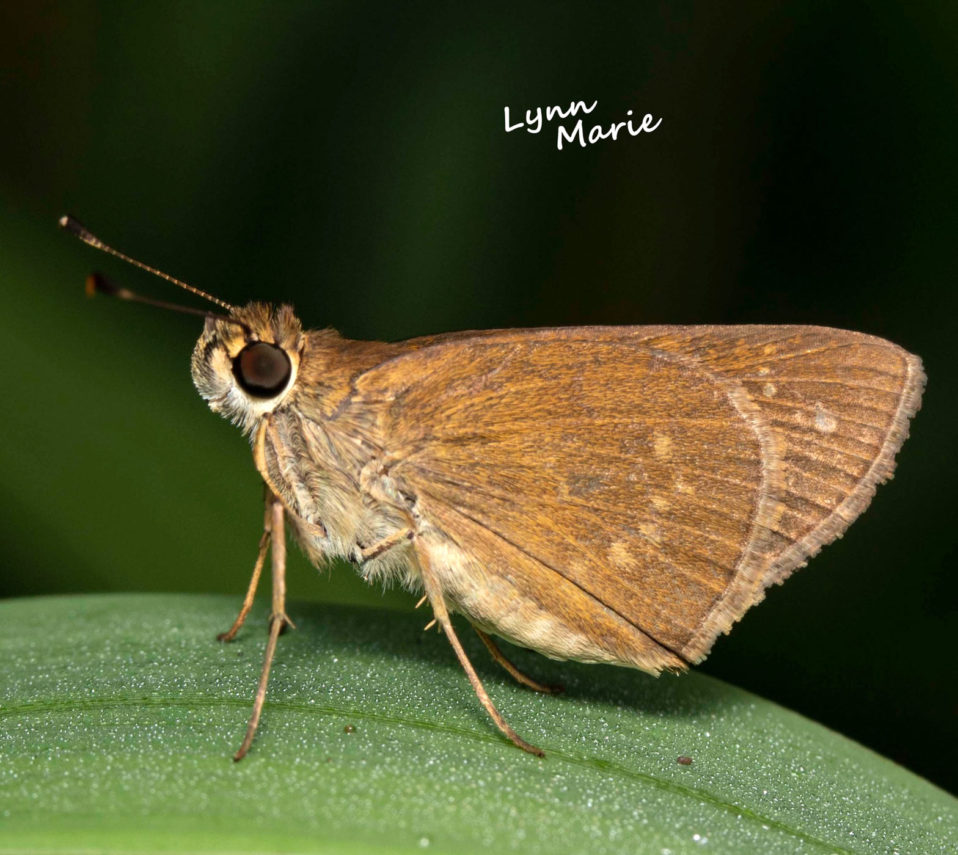
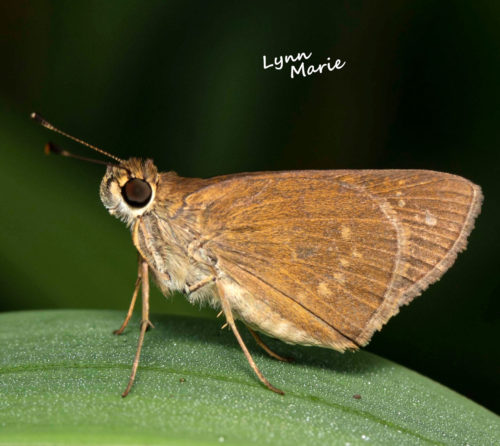
Three spotted Skipper
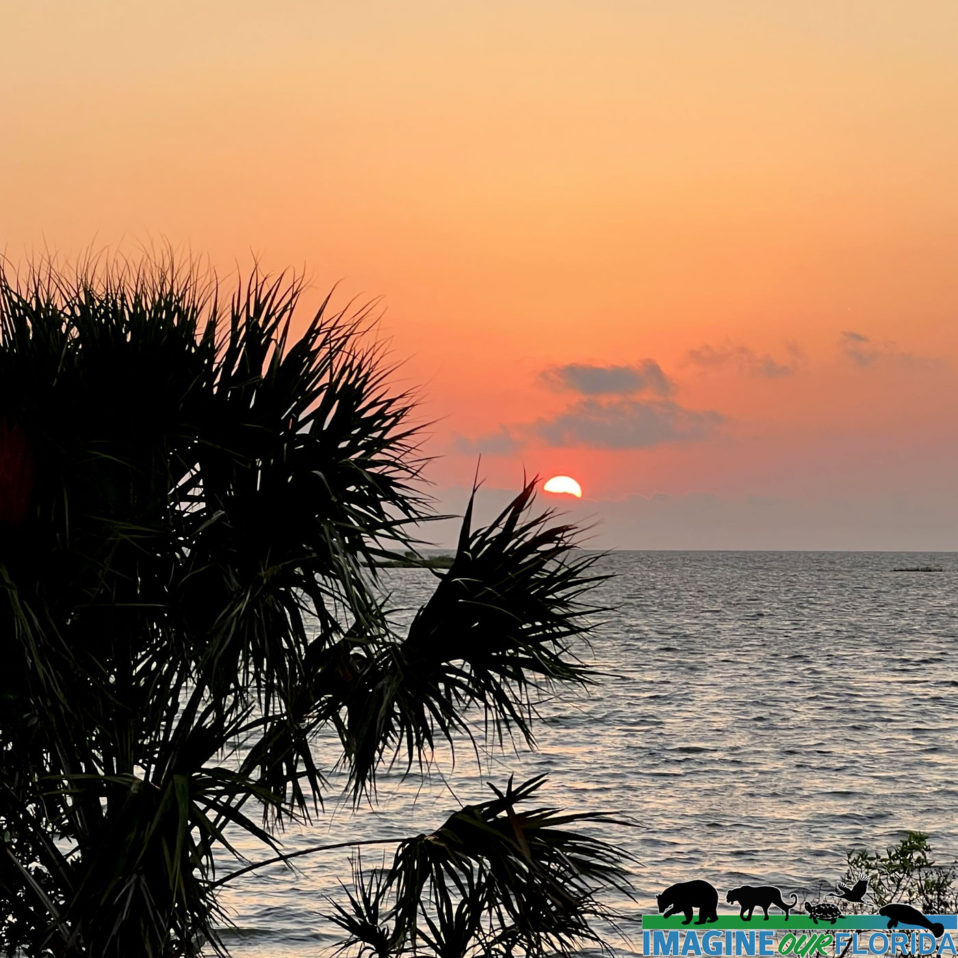
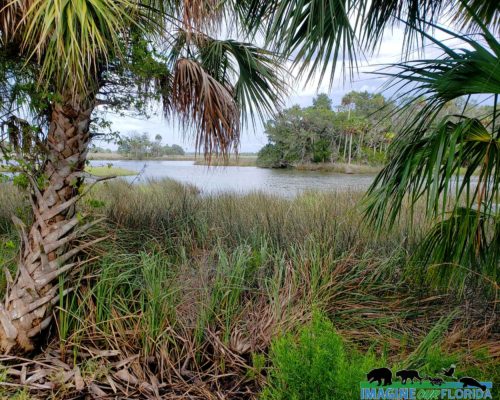
Follow That Dream Parkway to Bird Creek Beach
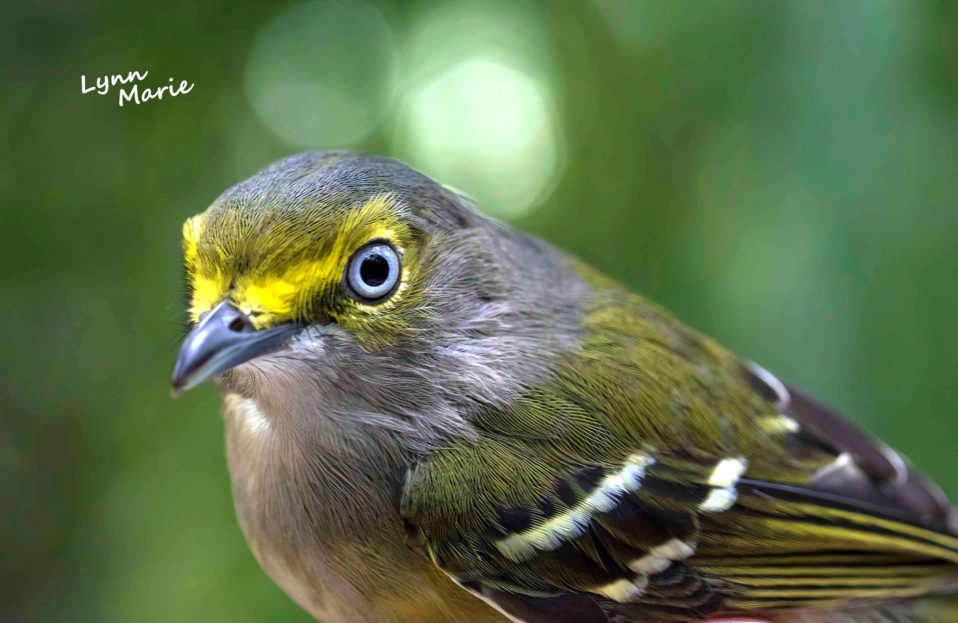
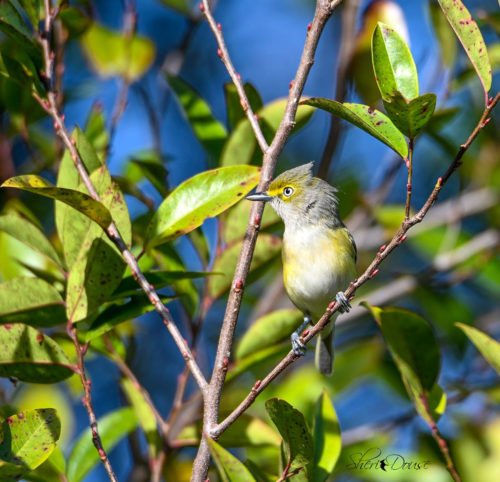
White-eyed vireo
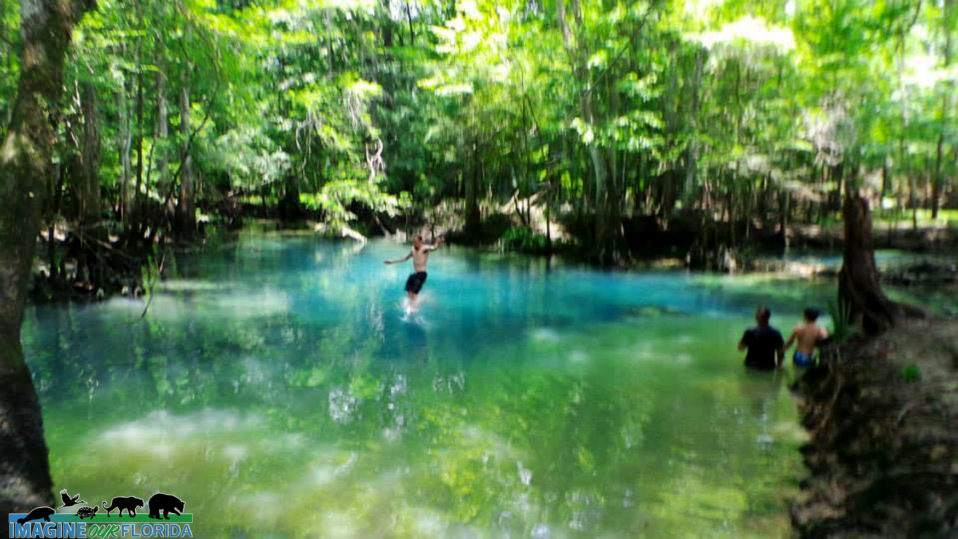
Blue Hole Spring
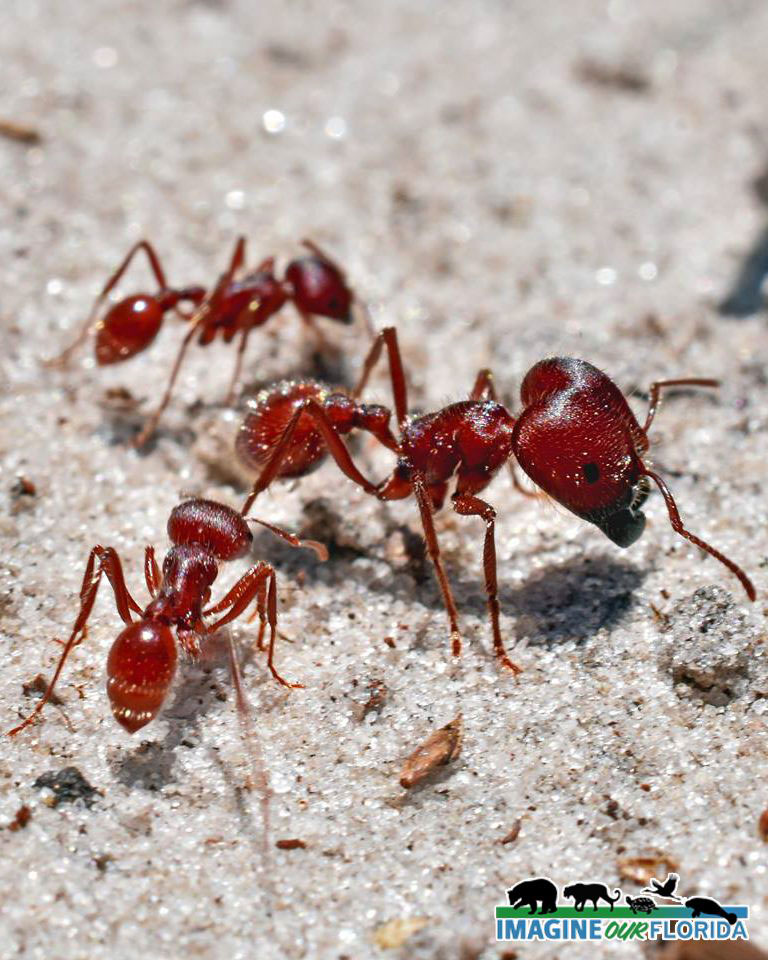
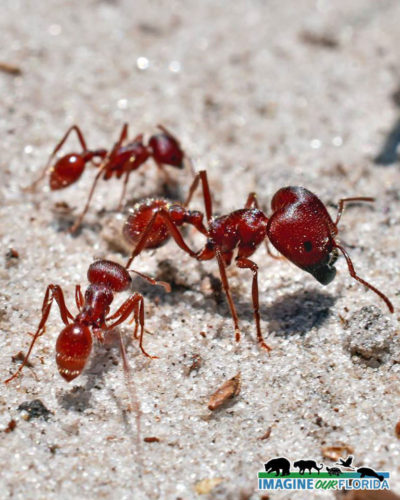
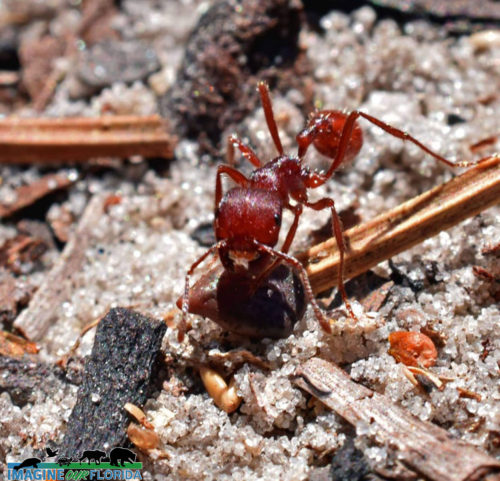
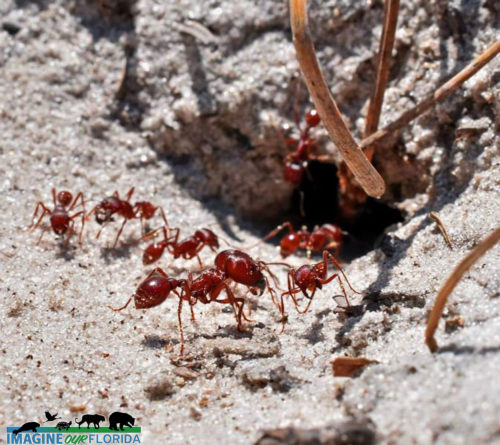
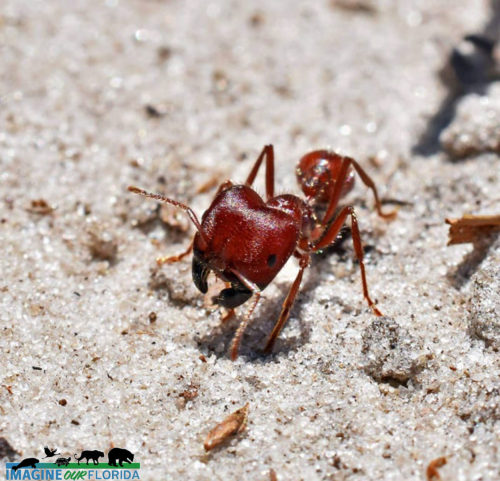
Florida Harvester Ant
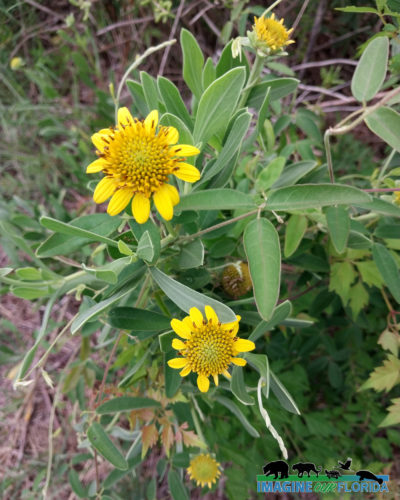
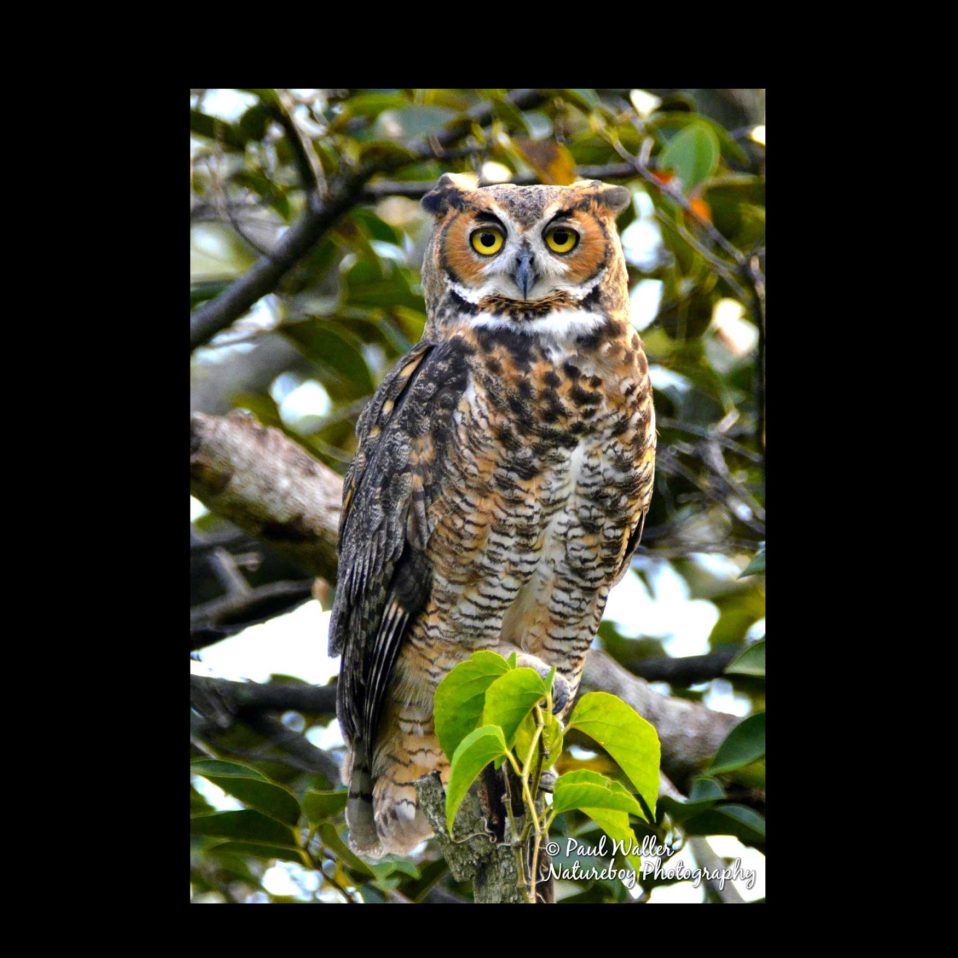
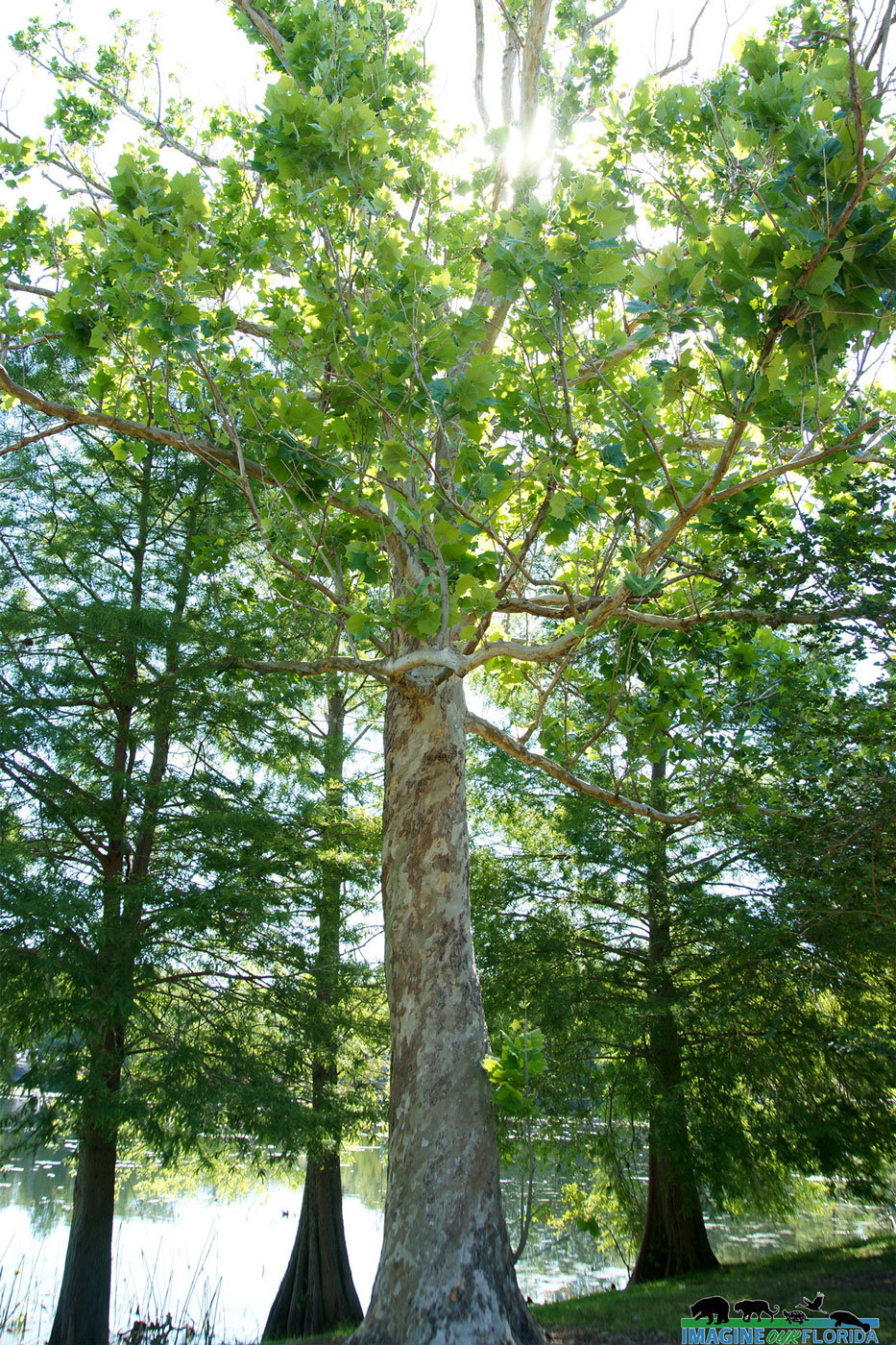
American Sycamore
The American sycamore, Platanus occidentalis, is a beautiful tree that grows 100 – 170 feet tall with a diameter of 3-14 feet. Its bark is white at first but turns brown as it grows. As the tree ages, the scales fall away and reveal the whitish-green bark beneath. Its distinctive leaves and green globe-shaped fruit make it easy to recognize. Songbirds dine on the seeds.
Sycamore trees are native from southern Canada to northern Florida. However, the tree has been planted far south of its range in Florida. The tree pictured in these images is located at Lake Lily in Central Florida.
Sycamore trees are known for their hurricane resistance and the ability of their intertwining root system to stabilize erosion. This makes them perfect specimens to plant in parks near waterways. The trees also tolerate acidic soils and as a result, they have been planted at phosphate mining sites. Before planting this beautiful shade tree in your yard, consider the height as well as the debris from falling bark and fruit.
Photo credit: Dan Kon
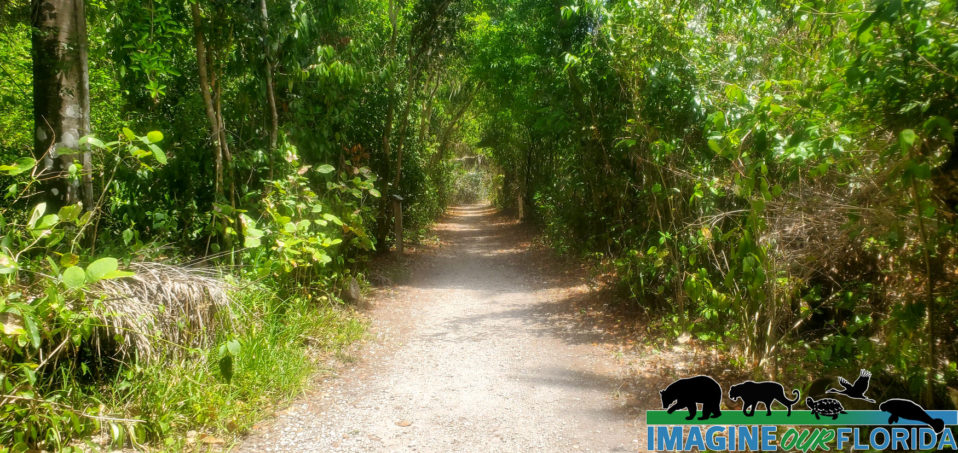
Collier-Seminole State Park
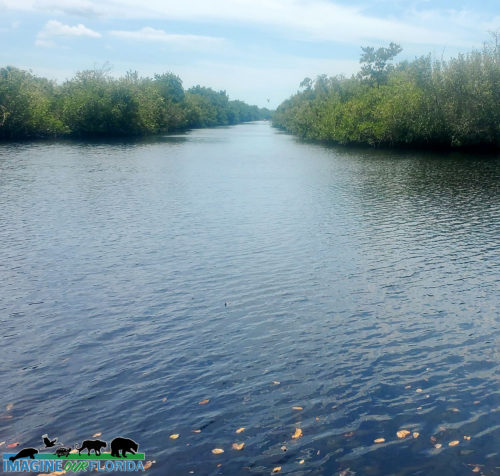
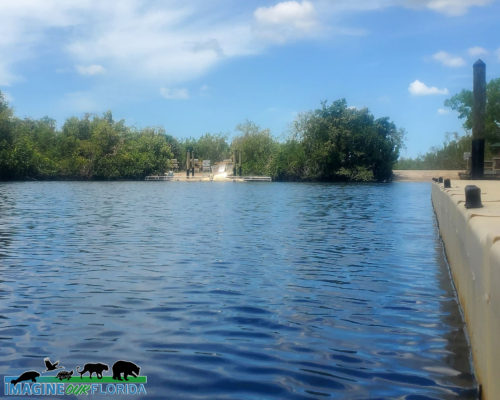
Collier-Seminole State Park, located in Naples, is a 7,271-acre park that offers the opportunity to explore part of the Great Mangrove Swamp of South Florida and an original stand of royal palms. Discover wildlife and wildflowers like those in the Everglades.
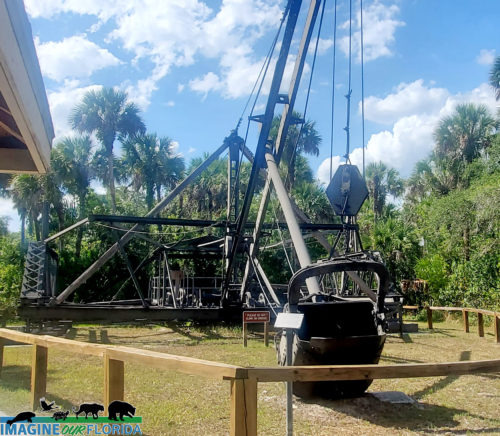
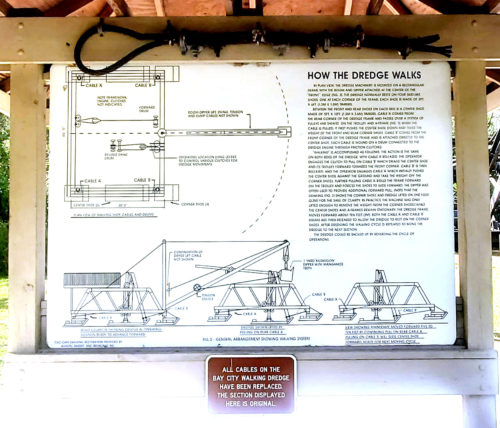
Learn about the Bay City Walking Dredge No. 489, a mechanical engineering marvel that walked forward as it dredged limestone to create a road from Tampa0 to Miami.
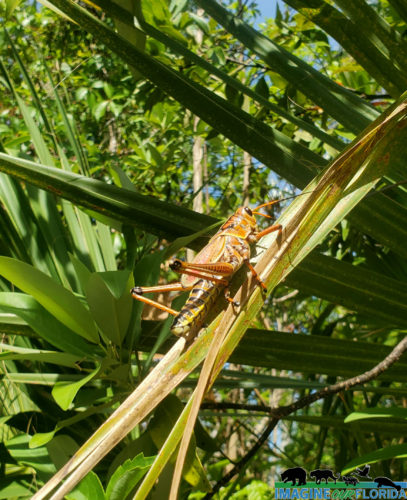
Collier-Seminole State Park has four wonderful nature trails ranging from less than a mile on the Royal Palm Hammock Nature Trail to the 5.25 mile Strand Swamp Trail. Discover the plants and animals, many imperiled, that live in the park. The park is designated a Great Florida Birding and Wildlife Trail so be sure to bring your camera/binoculars.
Launch your canoe or kayak at the ADA accessible launch. Explore the Blackwater River on the 13.5-mile canoe trail. As you paddle through the mangroves to Blackwater Bay, look for crocodiles, alligators, otters, manatees, and a variety of wading birds.
Primitive camping sites and campsites for your RV and tents are available. There are bike trails, two pavilions, picnic tables, and a playground for your enjoyment. Leashed pets are welcome.
For more information: https://www.floridastateparks.org/…/collier-seminole-state-…
Photo Credit: Ileana Rodriguez























































Recent Comments