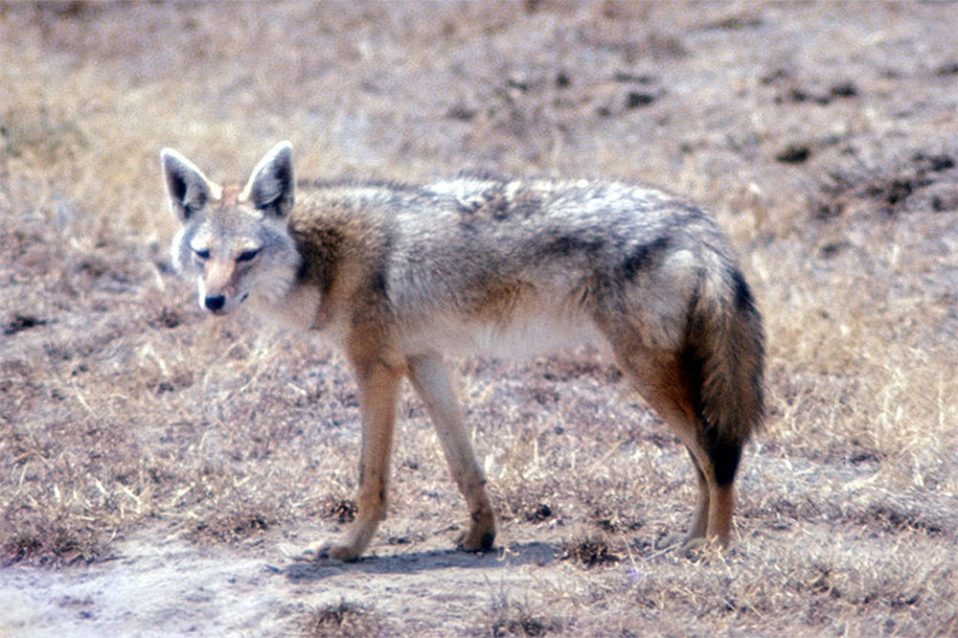
The coyote (Canis latrans) is a medium-sized omnivore. The average size of a coyote in Florida is about 28 lbs. Fossils of their remains have been found in Florida as far back as 2.6 million years ago. Due to the annihilation of the red wolves in Florida, coyotes are thriving. They are also stepping up to the plate to carry out the ecological task previously carried out by the red wolves. The role of a tertiary predator is important in maintaining balance and order in an ecosystem. They do this by regulating the trophic levels below them. If there are too many primary consumers, the vegetation can be depleted, causing soil and water problems. If there are too many secondary consumers, the primary consumer population can deplete, resulting in overgrowth. If prey isn’t available, coyotes adapt by eating vegetation.
February is part of the mating period. I suppose you could say Valentine’s Day is a romantic time for Coyotes as well as humans. After about a 63 day gestation period, the females will give birth. They will have to rely on the male to provide food for the mother and pups. The pups start weaning between April and May. This is done by eating the regurgitated food of their parents. By July, they are eating solid food. They begin hunting in August and will be ready to venture out on their own by December.
Coyotes are often called “song dogs” because of their variety of sounds. People frequently overestimate the number of coyotes in an area due to their singing. The phenomenon of hearing multiples is called the Beau Geste Effect. This term means “fine gesture” in French and comes from a book published in 1924. The story explains how a group of brothers used dead soldiers to give the illusion of several soldiers in an attempt to intimidate approaching forces.
Coyotes get a bad reputation, but with human behavior changes, we can learn to coexist with them. Don’t leave food out for other animals. Walk dogs on a short leash if you know coyotes are around. Secure trash. Keep your yard clear of any debris they could use as a den: secure livestock and their feed. If you see coyotes, make a loud noise to scare them away. As we learn to live with coyotes, we can learn to appreciate the role they play in keeping Florida’s ecosystems healthy.
Coyotes are a perfect example of an omnivore because they will eat almost anything. Their meals consist of plants, berries, dead things, insects (they love bugs), rodents, foxes, small animals of any kind including birds, small livestock, cats and small dogs, and of course, human and pet food!
Unlike wolves, coyotes do not hunt in packs. However, they will hunt with family members until their siblings go on their way.
Why are we seeing more coyotes in Florida? Humans have killed most of the wolves. Because wolves are now nearly extinct in Florida, coyotes have moved in and become king of the hill. They have no natural predators and will coexist in the wild with other animals, including panthers and bobcats. Coyotes love open grassy areas where rodents and other small animals live. Since man has cleared out many forests to make way for ranching and farming, the coyote has a free-range with plenty of food.
An adult coyote weighs 25 to 40 lbs. At times they may appear to be starving and seem very thin. This is their body build. Since they are extremely adaptable to almost any environmental condition and will eat almost anything, there is never any worry about coyotes finding enough food. When coyotes inhabit a new area, their population will grow quickly. Five to six pups may be born in a single litter. Once an area is established, the coyote population will level off.
Can we send them back to their original range? It has been tried in many states for hundreds of years, and the answer is no. Snare traps will most likely catch some other wild animal or someone’s pet before it captures a coyote. Two Florida black bears were found dead with coyote snares around their necks here in Central Florida. If we kill them, coyotes will just have more pups to repopulate the area quickly. Unless we reintroduce their natural predator, the red or grey wolf, and allow nature to take its course through Trophic Cascade, coyotes are here to stay.
What can you do to keep them wild and in the forests or uninhabited areas? We use the same techniques for coyotes as we do for our amazing Florida Black bears. Take in pet food and bird feeders, secure all attractants, scare that coyote if it is in your yard by yelling at it, making loud noises, etc. Never leave small pets outside unattended. Coyotes don’t know the difference between a small cat or dog and any other prey. It’s our responsibility as pet owners to keep pets safe.
Let’s learn to respect nature, and not fear it, to coexist and not destroy it.


Like this:
Like Loading...

















































































































































































 onia
onia







































































































































































Recent Comments